How does hyperbaric oxygen therapy work?
While breathing 100% oxygen as the body is exposed to increased atmospheric pressure, the oxygen molecules become condensed. This allows to breathe a higher partial pressure of oxygen. In turn, the oxygen dissolves in the plasma 10-15 times greater than normal.
This super-saturation of oxygen in the body’s tissues promotes:
- Increased capillary growth
- Increased white blood cell activity
- New tissue development
- Edema reduction by vasoconstriction
- Increase oxygen tension in hypoxic areas
- Blocks cytotoxic effects of carbon monoxide
- Blocks hypoxia associated with cyanide poisoning
- Reduction in the size of gas bubbles
- Numerous other physiological effects
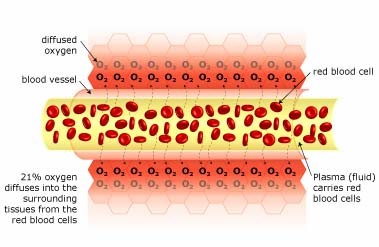
Normal Blood Flow
There is 21% oxygen in the air that we breathe, and our lungs transfer this oxygen to our red blood cells (via hemoglobin). These oxygen-filled red blood cells are carried around the body by the plasma (fluid), which travels through the blood vessels. The oxygen diffuses into the surrounding tissue ensuring that it is delivered to where it is needed most.
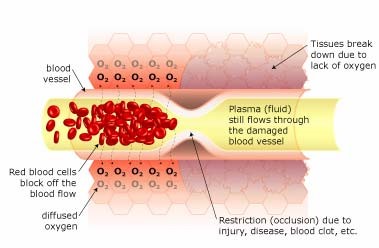
Restricted Blood Flow
When there is a restriction (occlusion) in blood flow due to surgery, illness, or injury, the red blood cells block the blood vessel and are unable to transfer oxygen to the cells on the other side of the occlusion. This causes swelling and starves the area of oxygen, causing hypoxia (a lack of oxygen); when this occurs, the tissue begins to break down.
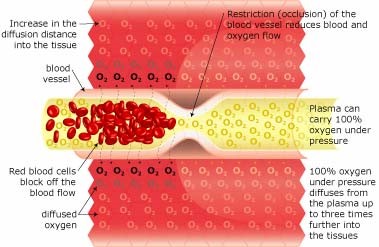
Hyperbaric Oxygenation
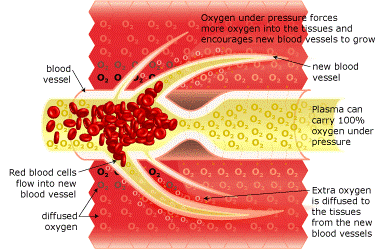
Breathing 100% oxygen under pressure causes the oxygen to diffuse into the blood plasma. This oxygen-rich plasma is able to travel past the restriction, diffusing up to 3 times further into the tissue. The pressurized environment helps to reduce swelling and discomfort, while providing the body with at least 10-15 times its normal supply of oxygen to help repair tissue damaged by the original occlusion or subsequent hypoxic condition. Hyperbaric Oxygenation (HBOT) directly increases the saturative effects of tissue oxygenation slowing and reversing hypoxic induced apoptosis – restoring blood supply to the compromised region by the development of new capillary networks (angiogenesis) enabling the body to alter the course and impact of the disease process.
Neurovascular Regeneration
HBOT mobilizes the body’s circulating stem cells. American Journal Physiology – Heart and Circulatory Physiology (Nov 05)] reports a single 2-hour exposure to HBOT at 2 ATA doubles circulating CD34+ progenitor stem cells (primordial cells targeted to salvage and restore damaged structures); and at approx. 20-hours of HBOT; circulating CD34+ cells increase eight-fold (800%).
What is a monoplace chamber?
The monoplace chamber is designed to house a single patient. It features a pneumatic control system and a unique full length, acrylic observation window. Full 360-degrees vision is maintained, as well as two-way communication with the operator. The chamber is normally pressurized with 100% oxygen thus relieving the patient from wearing an uncomfortable and cumbersome mask or hood for the entire treatment. During treatment the patient remains lying comfortably on a specialized contoured bed.
Chambers are typically inspected yearly by an outside independent company and uphold the highest training, safety, maintenance and service protocols available.
Who can benefit from Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy?
The range of clinical conditions responding favorably to HBOT is growing rapidly. Many individuals have shown vast improvements with HBOT, and the results are generally based on patient treatment outcomes rather than scientific studies. Often these chronic medical conditions languish in an individual’s life unless the individual requests that HBOT be added to their overall health care program.
What are the benefits of Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT)?
In somewhat more scientific terms:
- A Single 2-hour exposure to HBO at 2 ATA doubles circulating CD34+stem cells – primordial cells targeted to salvage and restore damaged structures. (Thom et al. American Journal of Physiology Nov,2005)
- After 20 treatments, circulating CD34+ stem cells increase up to eightfold (800%). (Thom et al. American Journal of Physiology Nov,2005)
- HBO stops Hypoxia Inducible Factor – 1 alpha (HIF-1a) and Hypoxia Inducible Factor – 1 beta (HIF-1?) from binding through the von Hippel-Lindau (VHL) process – the key proteins that create redness, swelling and pain. Carl Nathan Department of Microbiology and Immunology Weil Medical College, Cornell University. Oxygen and the inflammatory cell Nature, Vol. 422 April 17, 2003.
- HBO creates oxygenation in tissue up to 2,000% – this provides immediate help to ischemic and compromised tissue even with marginal blood flow.
- Bactericidal and Bacteriostatic – Hyperoxygenation of the tissues enhances killing of bacteria and is critical in curing deep-seated, resistant infections.
- Vasoconstriction – HBO vasoconstricts the small vessels in the body, especially in injured tissues. This decreases edema and is important in the treatment of burns, crush injuries and injured tissue in general.
- Angiogenesis – HBO creates collateral blood flow, critical to injured tissues. Collateral blood vessels are produced by increased fibroblasts leading to collagen. Therefore, creating new vascularization in ischemic, injured tissues, these new collateral blood vessels are functional as opposed to the collateral blood vessels from hypoxic tissue or ischemic tissue, which are nonfunctional.
- Antibiotic Synergy – HBO creates synergy with the following antibiotics: Fluoroquinolones, aminoglycosides and amphotericin B. These antibiotics use oxygen to transport across cell membranes.
- Decreased Lactic Acid – HBO decreases lactate accumulation in ischemic tissue, which greatly aids healing.
- Decrease in Inflammation – Not only does HBO block the binding of HIF-1alpha and HIF-1beta but decreases inflammation through several other mechanisms. Cytokines and other inflammatory chemicals, including lactic acid, are cleared with HBO. Oxidative Stress Markers and C-Reactive Protein were reduced with HBO. HBO also stimulates the body’s immune system to help clear inflammation. (BioMed central)
Please Note: A prescription is required for Hyperbaric Oxygen
What is a treatment like?
Once a patient is in the chamber and the door is closed, the oxygen begins to circulate. This starts a gradual increase in pressure — called compression. The oxygen circulation produces a relaxing sound much like the wind blowing through trees. There may be some slight warmth, but that is temporary. The Chamber Operator remains by the chamber throughout the treatment to adjust the rate of compression according to patient tolerance and to coach the patient on relieving the full sensation in the ears. You may feel fullness in your ears as your eardrums adjusts to the change in the chamber pressure. This is very similar to the feeling you experience when you are in an airplane or elevator. Compression generally lasts 10 minutes depending on how effective one is at clearing their ears.
When the interior of the chamber reaches the prescribed pressure, the fullness sensation in the ears will cease and the patient is free to rest or sleep. The chamber environment remains at room temperature. The patient may also use their personal entertainment system which includes a flat screen television monitor, DVD, CD, MP3 and VHS player. You may also have to wear a mask intermittently for a procedure called an air-break.
Near to the end of the treatment, the Chamber Operator will gradually decrease pressure that was added at the beginning. This is decompression, which generally lasts 10 minutes. During decompression, there may be a slight “popping” sensation in the ears because of the changing (decreasing) pressure. This “popping” is a normal adjustment, similar to what happens when driving up a mountain or ascending in an airplane. It is usually much easier to equalize ear pressure during decompression than during the compression phase.
What is a treatment like?
The length and frequency of treatments will be individualized for each patient and their condition. For most conditions patients are treated once or twice a day — Monday through Friday — and treatments may last 1 – 2 1/2 hours. Some emergency conditions will require only one or two treatments. In most cases of wound healing support, the effects are gradual, and 20 to 40 treatments may be required.
What side effects are possible?
The most common potential side effect during treatment is barotrauma to the ears and sinuses caused by pressure changes. To minimize this potential side effect, patients learn techniques to promote adequate clearing of the ears during compression (similar to clearing your ears on an airplane).
Other side effects are rarer but may include oxygen toxicity which affects only 1 person in 10,000. After many treatments some changes in vision may be noticed by a few patients. Any changes usually return to pre-treatment vision levels in a 6-week period. Some patients may experience claustrophobia which can be resolved with relaxation techniques or mild medications. Also, HBOT may induce accelerated maturation of cataracts.
In addition, a few patients report a “popping” or “cracking” sensation in their ears between treatments. This sensation can be relieved using the same techniques that patients use to clear their ears while they are in the chamber.
What can be taken into the chamber?
Since patients are enclosed within 100% oxygen environment, multiple safety precautions are followed to promote safety. Cigarette lighters, matches, nylon wigs, hairpieces, petroleum ointments, hearing aids, makeup, hair spray, synthetic clothing, hard contact lenses and paper products cannot be taken into the chamber. Patients are provided with 100% cotton scrubs to wear during treatments.
How are patients accepted for treatment?
Patients are accepted either by self-referral or by physician referral. A prescription is required for HBOT treatment. Patients schedule directly with the clinic.
Patients are evaluated and treated based on their specific needs and condition. The facility’s medical director works with other clinicians as required so that the hyperbaric treatments are coordinated with any other therapies.
Does insurance cover the cost of hyperbaric oxygen therapy?
HBOT costs may be covered by insurance. Most health insurers and Medicare recognize HBOT as being medically appropriate and usually cover conventional conditions [FDA-approved, “on-label” conditions. Typically, alternative conditions [“off-label” indications] are non-reimbursable; however, the physician consultation as well as pre- and post-treatment diagnostic tests may be covered. Each clinic can discuss insurance possibilities.
What is a Bag Chamber?
A bag chamber, sometimes referred to as soft chamber, mild hyperbaric chamber or Gamow bag, has FDA “510(k)” clearance for marketing only for the treatment of acute mountain sickness (AMS) where at higher elevations there is less oxygen in the air and climbers become ill. Most of these devices are portable and are made from urethane-coated nylon which is sealed with a dual-zipper and design to treat at no greater than 4 psig of pressure (which equals 1.27 ATA or 9 feet of depth).
As an FDA Class II medical device, a licensed physician (MD or DO) prescription is mandatory for any use or purchase of the bag chamber. In addition, most States fire safety compliance is mandated in accordance with the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA) 99. Some States follow NFPA 101 Life Safety Code which invokes compliance with NFPA 99. This means the local fire marshal can insist that any clinic that uses hyperbaric chambers, including bag chambers, comply with codes which require the installation of fire walls, certified fire doors, sprinklers and other code compliance items.
The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) also mandates that all chambers that can increase pressure over 2 psig are designed to specific fabrication codes and be certified by the Pressure Vessel for Human Occupancy (PVHO-1) and embossed with the PVHO-1 stamp. Most soft chambers have not been able to demonstrate that they comply with any recognized hyperbaric chamber design or fabrication standard.
The TreatNOW Coalition recommends patients with Concussion/TBI/PTSD get treatment in hard shell chambers.
Disclaimer: The information provided by this website does not constitute a medical recommendation. It is intended for informational purposes only, and no claims, either real or implied, are being made.